Unveiling the Tail of Spence: A Comprehensive Guide
The tail of Spence, also known as the axillary process, is an extension of the breast tissue that extends into the axilla (armpit). While often overlooked, this anatomical feature plays a crucial role in breast health and can be a site for various breast-related conditions. This comprehensive guide delves into the anatomy, significance, clinical relevance, and potential issues associated with the tail of Spence, providing you with a thorough understanding of this essential part of the breast.
This article provides unique value by offering an in-depth exploration of the tail of Spence, bridging the gap between basic anatomical knowledge and practical clinical considerations. Whether you’re a medical professional, a student, or simply seeking to understand your own body better, this resource will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the complexities of breast health.
Anatomical Overview of the Tail of Spence
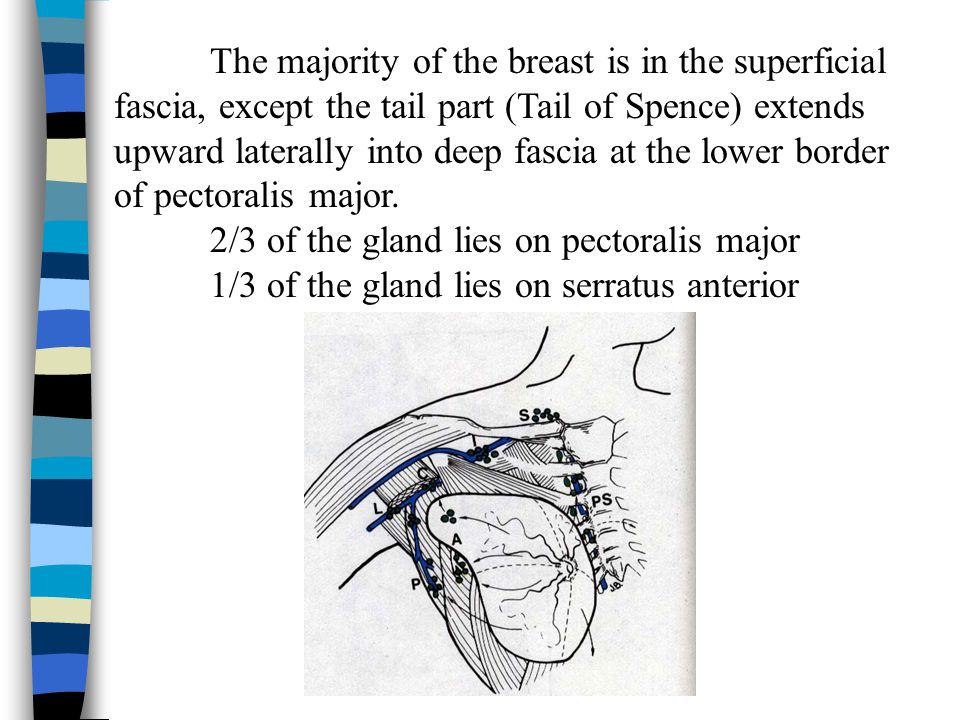
The tail of Spence is not a separate structure but rather a continuation of the glandular tissue of the breast that extends upwards and outwards towards the armpit. It’s named after James Spence, a Scottish surgeon who first described it in detail. Understanding its location and composition is crucial for recognizing its potential clinical significance.
The tail of Spence consists primarily of:
- Glandular Tissue: This is the functional tissue of the breast, responsible for milk production (in lactating women).
- Fibrous Tissue: Provides support and structure to the breast.
- Fatty Tissue: Contributes to the overall size and shape of the breast.
- Blood Vessels and Nerves: Supply nutrients and sensation to the breast tissue.
- Lymphatic Vessels: Part of the lymphatic system, which plays a crucial role in immune function and fluid drainage. The lymphatic drainage from the tail of Spence is particularly important, as it often drains to the axillary lymph nodes.
The size and prominence of the tail of Spence can vary significantly from person to person, influenced by factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, and body composition. In some individuals, it may be barely noticeable, while in others, it can be quite prominent and even mistaken for a separate mass.
Location and Boundaries
The tail of Spence extends from the upper outer quadrant of the breast, passing through an opening in the deep fascia (a layer of connective tissue) near the border of the pectoralis major muscle (the large muscle of the chest). This opening is sometimes referred to as the foramen of Langer. The tail of Spence then continues into the axilla, where it intermingles with the axillary fat pad.
Clinical Significance of the Tail of Spence
The tail of Spence is clinically significant for several reasons, primarily because it is a common site for breast-related conditions, including benign and malignant lesions. Its proximity to the axillary lymph nodes also makes it an important area to consider when assessing breast cancer staging and treatment.
- Breast Cancer: The tail of Spence is a frequent location for breast cancer to develop. This is likely due to the relatively high concentration of glandular tissue in this area.
- Benign Breast Conditions: Fibrocystic changes, fibroadenomas, and other benign breast conditions can also occur in the tail of Spence.
- Lymph Node Involvement: Because the lymphatic vessels from the tail of Spence drain to the axillary lymph nodes, any cancer cells that spread from this area are likely to involve these nodes. This can affect the staging and treatment of breast cancer.
- Mastalgia (Breast Pain): Pain in the tail of Spence can be a symptom of various breast conditions, including hormonal changes, inflammation, or infection.
- Accessory Breast Tissue: In some cases, individuals may have accessory breast tissue (also known as polymastia) in the axilla, which can be mistaken for the tail of Spence.
Understanding Breast Cancer Screening and the Tail of Spence
Regular breast cancer screening, including mammograms and clinical breast exams, is crucial for early detection of breast cancer in the tail of Spence. It’s important to inform your healthcare provider if you notice any changes in this area, such as a lump, thickening, pain, or nipple discharge.
Mammography Considerations
During a mammogram, the breast is compressed to obtain clear images. It’s essential that the mammogram includes the tail of Spence to ensure that any abnormalities in this area are detected. Inform the technician if you have a prominent tail of Spence, as they may need to adjust the positioning to ensure adequate visualization.
Self-Exams and Clinical Exams
Performing regular breast self-exams can help you become familiar with the normal texture and anatomy of your breasts, including the tail of Spence. This can make it easier to detect any new or unusual changes. During a clinical breast exam, your healthcare provider will also examine the tail of Spence for any abnormalities.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques for the Tail of Spence
Several diagnostic imaging techniques can be used to evaluate the tail of Spence, depending on the clinical situation. These include:
- Mammography: As mentioned above, mammography is the primary screening tool for breast cancer.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound can be used to further evaluate any abnormalities detected on mammography or during a clinical exam. It’s particularly useful for distinguishing between solid and cystic masses.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI is a more sensitive imaging technique that can be used to evaluate the tail of Spence in certain situations, such as in women with dense breast tissue or those at high risk for breast cancer.
- Biopsy: If an abnormality is detected on imaging, a biopsy may be necessary to determine whether it is benign or malignant. Several types of biopsies can be performed, including fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, and surgical biopsy.
Treatment Options for Conditions Affecting the Tail of Spence
The treatment for conditions affecting the tail of Spence depends on the specific diagnosis. Benign conditions may require no treatment or may be managed with pain medication or hormone therapy. Malignant conditions, such as breast cancer, may require a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy.
Surgical Considerations
If surgery is necessary to remove a tumor in the tail of Spence, the surgeon will take care to preserve as much normal breast tissue as possible. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove the axillary lymph nodes to check for cancer spread. This procedure is called axillary lymph node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy.
The Role of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is a surgical procedure used to determine whether cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes. The sentinel lymph node is the first lymph node that cancer cells are likely to spread to from the primary tumor. During SLNB, the surgeon injects a radioactive tracer or blue dye near the tumor. The tracer or dye travels through the lymphatic vessels to the sentinel lymph node, which is then removed and examined under a microscope. If the sentinel lymph node is free of cancer, it’s likely that the other axillary lymph nodes are also free of cancer, and no further lymph node dissection is necessary.
Understanding Breast Augmentation and the Tail of Spence
Breast augmentation, also known as augmentation mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure to increase the size or change the shape of the breasts. While breast implants are typically placed beneath the breast tissue or the pectoral muscle, it’s important to consider the potential impact on the tail of Spence.
Implant Placement and Tail of Spence
The surgeon will carefully consider the anatomy of the tail of Spence when planning the implant placement. In some cases, the implant may compress or distort the tail of Spence, which can cause discomfort or alter its appearance. It’s important to discuss these potential risks with your surgeon before undergoing breast augmentation.
Tail of Spence Pain Management
Pain in the tail of Spence, also known as mastalgia, can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal changes, fibrocystic changes, inflammation, or infection. Treatment options for mastalgia include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Supportive bra: Wearing a well-fitting, supportive bra can help reduce breast pain.
- Heat or cold therapy: Applying a warm compress or ice pack to the affected area can help relieve pain.
- Hormone therapy: In some cases, hormone therapy may be necessary to manage mastalgia caused by hormonal imbalances.
- Prescription pain medication: If over-the-counter pain relievers are not effective, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medication.
The Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider, including clinical breast exams, are essential for maintaining breast health and detecting any potential problems early. Be sure to discuss any concerns you have about your breasts, including the tail of Spence, with your doctor.
Debunking Myths About the Tail of Spence
Several myths surround the tail of Spence, often causing unnecessary anxiety. Let’s address some common misconceptions:
- Myth: A prominent tail of Spence is always a sign of cancer.
Fact: A prominent tail of Spence can be a normal anatomical variation. However, any new or changing lumps should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. - Myth: Pain in the tail of Spence is always a sign of cancer.
Fact: Pain in the tail of Spence is more commonly caused by benign conditions, such as hormonal changes or fibrocystic changes. However, persistent or unexplained pain should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. - Myth: The tail of Spence is not important for breast cancer screening.
Fact: The tail of Spence is an important area to include in breast cancer screening, as it is a common site for breast cancer to develop.
Breast Health and Self-Care: Tail of Spence Considerations
Beyond medical interventions, several self-care practices can contribute to breast health, including being mindful of the tail of Spence:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Eat a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of breast cancer.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity has been shown to reduce the risk of breast cancer.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Don’t smoke: Smoking is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Practice stress management: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of various health problems, including breast cancer.
Practical Advice to Take Care of your Breast
Understanding the tail of Spence empowers you to take proactive steps in monitoring your breast health. Regular self-exams, coupled with awareness of any changes, can significantly contribute to early detection and timely intervention. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. By staying informed and proactive, you can safeguard your breast health and well-being.
