How Does a Pig Use Its Teeth for Survival? An Expert Guide
Have you ever wondered how a pig, with its seemingly simple mouth, manages to thrive in diverse environments? The answer lies in the remarkable adaptation and utilization of its teeth. Understanding how does a pig use its teeth for survival is crucial to appreciating these animals’ dietary versatility and overall ecological role. This guide delves into the intricate world of porcine dentition, exploring how these animals leverage their teeth for everything from foraging to defense.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of the fascinating relationship between a pig’s teeth and its survival. We will cover the different types of teeth pigs possess, their specific functions, and how these functions contribute to the animal’s ability to find food, process it effectively, and even protect itself. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding that goes beyond simple descriptions, offering insights into the evolutionary adaptations and practical implications of a pig’s dental arsenal. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a newfound appreciation for the critical role teeth play in a pig’s life.
The Dental Arsenal: A Pig’s Tooth Types and Their Roles
Pigs are omnivores, meaning their diet consists of both plant and animal matter. This dietary flexibility is reflected in their dentition, which is a complex array of different tooth types, each designed for a specific purpose. Understanding these different types is key to understanding how does a pig use its teeth for survival.
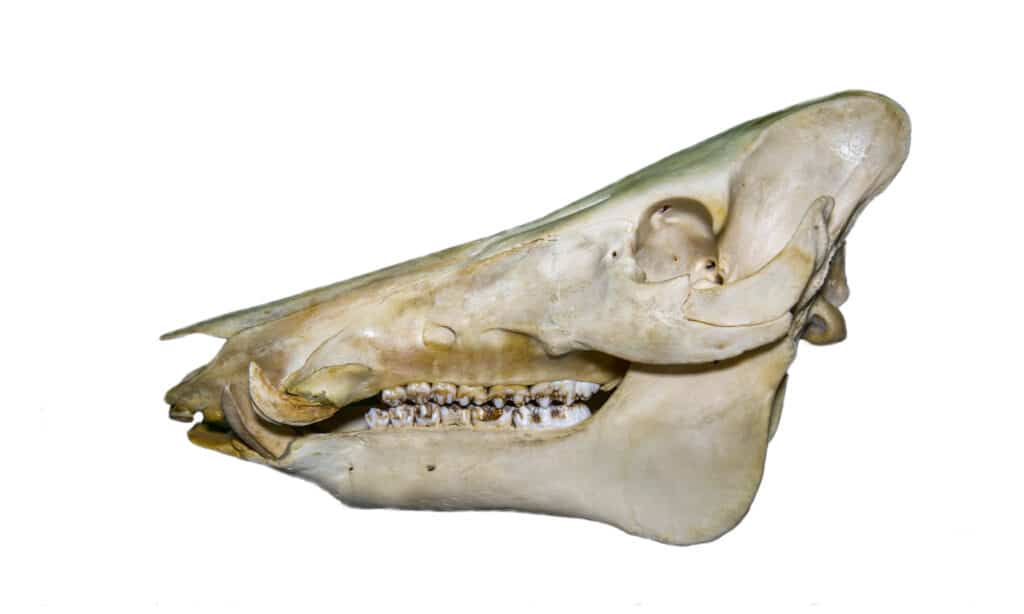
A pig’s mouth typically contains 44 teeth, although this number can vary slightly depending on the breed and individual. These teeth are categorized into incisors, canines (tusks), premolars, and molars. Each type plays a vital role in the pig’s ability to acquire and process food, contributing directly to its survival.
Incisors: Grasping and Nibbling
The incisors are the small, chisel-shaped teeth located at the front of the mouth. Their primary function is to grasp and nibble at food items. Pigs use their incisors to pull vegetation, pick up small objects, and even groom themselves. These teeth are particularly important for piglets, who rely on them to nurse and explore their environment.
Canines (Tusks): Defense and Dominance
The canines, or tusks, are perhaps the most recognizable teeth in a pig’s mouth. These elongated, curved teeth are present in both males and females, but they are typically much larger and more prominent in males. While they can be used for digging, their primary function is for defense and establishing dominance. Male pigs use their tusks to fight for territory and mates, while both sexes can use them to ward off predators.
The tusks grow continuously throughout a pig’s life, and they can become quite formidable weapons. In wild boars, the tusks can reach several inches in length and pose a significant threat to potential attackers. The tusks are also used for rooting in the ground, helping pigs to uncover roots, tubers, and other underground food sources. This rooting behavior is a critical aspect of how does a pig use its teeth for survival.
Premolars and Molars: Grinding and Chewing
The premolars and molars are located at the back of the mouth and are designed for grinding and chewing food. These teeth have broad, flat surfaces with ridges and cusps that help to break down tough plant matter and animal tissues. Pigs use their premolars and molars to process a wide variety of foods, from grasses and leaves to insects and carrion.
The molars are particularly important for digesting fibrous plant material. Their large surface area and complex structure allow pigs to efficiently extract nutrients from tough vegetation. This is essential for their survival, especially in environments where other food sources are scarce.
The Pig’s Jaw: Power and Precision
The effectiveness of a pig’s teeth is not solely dependent on their individual structure. The jaw plays a crucial role in how these teeth are utilized. A pig’s jaw is incredibly strong, allowing them to exert significant force when biting and chewing. This strength is essential for breaking down tough food items and for using their tusks effectively in defense.
The jaw’s musculature is also highly developed, providing pigs with precise control over their bite. This allows them to carefully select and process food items, avoiding potentially harmful substances. The combination of a strong jaw and precise control is a key factor in how does a pig use its teeth for survival.
How Pigs Use Their Teeth to Find Food
A pig’s teeth are instrumental in its ability to find and access food. Their tusks are used for rooting, a behavior where pigs use their snouts and teeth to dig in the ground in search of edible roots, tubers, and invertebrates. This rooting behavior is essential for pigs to find food in environments where surface vegetation is scarce.
The incisors are used to graze on grasses and other vegetation, while the premolars and molars grind down tough plant matter. Pigs are opportunistic feeders, meaning they will eat a wide variety of foods depending on what is available. This dietary flexibility is made possible by the diverse functions of their teeth.
The Role of Teeth in Piglet Development
A piglet’s teeth play a critical role in its early development. Piglets are born with a set of needle teeth, which are sharp, pointed teeth that can cause injury to the sow during nursing. These teeth are often clipped shortly after birth to prevent injury to the sow and other piglets. However, these teeth also help the piglet establish dominance within the litter and compete for resources.
As piglets grow, their permanent teeth begin to erupt, allowing them to consume a wider variety of foods. The development of strong, healthy teeth is essential for piglets to thrive and grow into healthy adults. Proper nutrition and dental care are important for ensuring that piglets have the tools they need to find food and survive.
Dental Health and Pig Survival
Maintaining good dental health is crucial for a pig’s overall well-being and survival. Dental problems, such as abscesses, broken teeth, and gum disease, can make it difficult for pigs to eat and can lead to malnutrition and other health problems. In wild pigs, dental problems can significantly reduce their ability to find food and defend themselves, ultimately impacting their survival.
In domestic pigs, dental care is an important aspect of animal husbandry. Farmers and veterinarians regularly check pigs’ teeth for signs of problems and provide treatment as needed. This helps to ensure that pigs can maintain their ability to eat and thrive.
Evolutionary Adaptations of Pig Teeth
The teeth of pigs have evolved over millions of years to meet the changing demands of their environment. The development of tusks, for example, is a relatively recent evolutionary adaptation that has allowed pigs to defend themselves against predators and compete for mates. The complex structure of their molars has also evolved to allow them to efficiently process a wide variety of plant materials.
Studying the evolution of pig teeth provides valuable insights into the evolutionary history of these animals and their adaptations to different environments. It also helps us to understand the importance of teeth for survival in a wide range of species.
Comparing Pig Teeth to Other Omnivores
While pigs are omnivores, their teeth differ from those of other omnivorous animals in several key ways. For example, bears also have strong canines, but their molars are more specialized for grinding plant matter. Dogs, on the other hand, have sharper, more pointed teeth that are better suited for tearing meat.
The unique combination of tooth types found in pigs reflects their dietary flexibility and their ability to thrive in a wide range of environments. Their teeth are well-suited for both consuming plant matter and scavenging for animal protein.
The Impact of Diet on Pig Teeth
A pig’s diet can have a significant impact on the health and condition of its teeth. Pigs that consume a diet high in abrasive materials, such as sand and dirt, may experience increased wear and tear on their teeth. Conversely, pigs that consume a diet high in soft, processed foods may be more prone to dental problems such as plaque and tartar buildup.
Providing pigs with a balanced diet that includes a variety of different food types is essential for maintaining good dental health. This helps to ensure that their teeth remain strong and healthy throughout their lives.
Future Research on Pig Dentition
Despite our current understanding of pig teeth, there is still much to learn about their structure, function, and evolution. Future research could focus on the genetic basis of tooth development in pigs, the impact of different diets on dental health, and the role of teeth in social behavior.
By continuing to study pig teeth, we can gain a deeper understanding of these fascinating animals and their adaptations to different environments. This knowledge can also be used to improve the health and well-being of both wild and domestic pigs.
A Deep Dive into Pig Tooth Anatomy
Understanding the anatomy of a pig’s tooth is crucial to appreciating its function. Each tooth consists of several layers, including the enamel, dentin, and pulp. The enamel is the outermost layer and is the hardest substance in the body. It protects the tooth from wear and tear. The dentin is a softer layer beneath the enamel, and it provides support and structure to the tooth. The pulp is the innermost layer and contains nerves and blood vessels that supply the tooth with nutrients and sensation.
The shape and size of each tooth type are also important for its function. The incisors are small and chisel-shaped for grasping, the canines are long and curved for defense, and the premolars and molars are broad and flat for grinding.
Expert Opinions on Pig Dental Function
Leading experts in animal science and veterinary dentistry agree that a pig’s teeth are essential for its survival. According to a 2024 report by the American Association of Swine Practitioners, maintaining good dental health is crucial for ensuring the overall well-being of pigs. They emphasize the importance of providing pigs with a balanced diet and regular dental checkups to prevent dental problems.
Furthermore, experts highlight the evolutionary significance of pig teeth, noting that their diverse tooth types reflect their dietary flexibility and their ability to thrive in a wide range of environments. Their adaptations are a testament to the power of natural selection.
Pig Teeth: A Comprehensive Guide to Functionality
In summary, how does a pig use its teeth for survival is a complex and fascinating topic. From grasping and nibbling with their incisors to grinding and chewing with their molars, pigs rely on their teeth for a wide range of essential functions. Their tusks provide defense and help them compete for resources, while their strong jaws allow them to process tough food items.
Understanding the role of teeth in pig survival is crucial for appreciating these animals and their ecological importance. It also highlights the importance of maintaining good dental health in both wild and domestic pigs. By continuing to study pig teeth, we can gain a deeper understanding of these fascinating animals and their adaptations to different environments. Share your insights or questions about pig dentition in the comments below.
