Unveiling the Mysteries of the Tartaria Map: A Comprehensive Exploration
The term “Tartaria map” evokes images of a lost civilization, a hidden history, and a global empire shrouded in mystery. For those delving into alternative history, conspiracy theories, or simply curious about cartographic anomalies, the Tartaria map serves as a potent symbol. But what exactly is a Tartaria map? What does it represent, and why does it continue to capture the imagination of so many? This article aims to provide a comprehensive, evidence-based exploration of the Tartaria map phenomenon, separating fact from fiction and offering a balanced perspective on its origins, interpretations, and enduring appeal. We’ll delve into the historical context, examine available cartographic evidence, and explore the various theories surrounding Tartaria, all while maintaining a critical and discerning approach.
Deciphering the Tartaria Map: Definition, Scope, and Historical Context
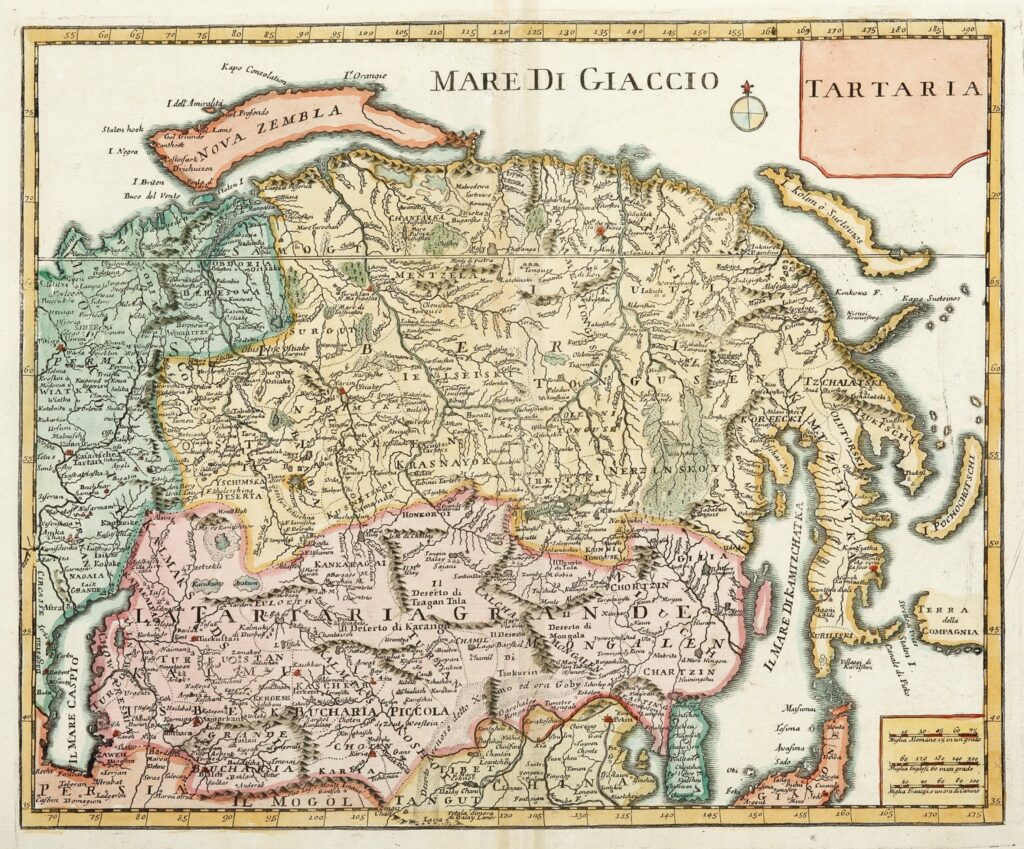
The term “Tartaria map” generally refers to historical maps, particularly those from the 16th to 19th centuries, that depict a vast region in Central Asia labeled as “Tartary” or “Tartaria.” This region typically encompasses areas of modern-day Russia, Siberia, Central Asia, and parts of Eastern Europe. The maps themselves vary significantly in detail and accuracy, reflecting the limited geographical knowledge of the time and the evolving understanding of the region by European cartographers.
It’s crucial to understand the historical context in which these maps were created. European knowledge of Central Asia during this period was often based on second-hand accounts, travelers’ tales, and incomplete surveys. Cartographers frequently relied on existing maps, sometimes copying errors or perpetuating myths. The representation of Tartaria on these maps should therefore be viewed as a reflection of European perceptions and understanding of a distant and largely unknown region, rather than a precise depiction of a unified empire or civilization.
The name “Tartar” itself has a complex history. It originated as a term used by Europeans to refer to various nomadic groups inhabiting Central Asia, including Mongols and Turkic peoples. Over time, the term became associated with the Golden Horde, the Mongol successor state that ruled over much of Russia and surrounding territories. The term “Tartary” thus became a general designation for the vast lands inhabited by these groups.
Some interpretations of the Tartaria map suggest that it represents a powerful, advanced civilization that was deliberately erased from history. Proponents of this theory often point to the size and prominence of Tartaria on historical maps as evidence of its importance. However, mainstream historians argue that the depiction of Tartaria on these maps reflects European ignorance and a tendency to lump together diverse groups under a single, broad label. The sheer size attributed to Tartaria on many maps is often seen as an indication of the limited knowledge of the area, rather than an accurate reflection of its political or cultural unity.
The Evolution of Cartographic Representations of Tartaria
Examining the evolution of Tartaria maps over time reveals a changing understanding of the region. Early maps often depict Tartaria as a largely blank space, with only a few major rivers and mountain ranges indicated. As European exploration and trade expanded, more detailed maps began to emerge, showing cities, settlements, and political divisions. However, even these later maps often contain inaccuracies and inconsistencies, reflecting the challenges of mapping such a vast and remote region.
One notable example is the work of Guillaume Delisle, a prominent French cartographer of the 18th century. Delisle’s maps were renowned for their accuracy and detail, and his depiction of Tartaria reflects a more nuanced understanding of the region than many earlier maps. He distinguished between different Tartar groups, such as the Independent Tartars and the Chinese Tartars, and provided more detailed information about the geography and political landscape of the area. However, even Delisle’s maps were not without their limitations, and his representation of Tartaria still reflects the challenges of mapping a region that was largely inaccessible to Europeans.
It is important to note that the maps themselves should be analyzed critically, taking into account the biases and limitations of the cartographers who created them. Maps are not simply objective representations of reality; they are products of their time, reflecting the political, cultural, and economic interests of the societies that produced them. Understanding the context in which these maps were created is essential for interpreting them accurately and avoiding unwarranted conclusions.
Tartaria and the Mud Flood Theory: A Critical Examination
The Tartaria map is often linked to the “mud flood theory,” a fringe theory that posits that a cataclysmic mud flood event wiped out a technologically advanced civilization in the 19th century. Proponents of this theory often point to the apparent lack of historical records documenting this event and the presence of strange architectural features in old buildings as evidence of its occurrence. They also claim that the Tartarian civilization was the victim of this mud flood, and that its history has been deliberately suppressed by mainstream historians.
However, there is no credible evidence to support the mud flood theory. The lack of historical records documenting such an event is easily explained by the fact that it simply did not happen. The architectural features cited as evidence of the mud flood can be attributed to a variety of factors, such as changes in building styles, renovations, and natural disasters. Furthermore, the claim that the Tartarian civilization was deliberately erased from history is contradicted by the fact that Tartaria is prominently featured on many historical maps.
The mud flood theory is a classic example of pseudoscience, relying on speculation, conjecture, and selective use of evidence to support its claims. It is important to approach such theories with a healthy dose of skepticism and to rely on credible sources of information when researching historical topics.
The Enduring Appeal of the Tartaria Myth
Despite the lack of evidence to support the existence of a lost Tartarian civilization, the Tartaria myth continues to resonate with many people. This enduring appeal can be attributed to a number of factors. First, the Tartaria myth offers a sense of mystery and intrigue, appealing to those who are drawn to alternative history and conspiracy theories. Second, the Tartaria myth provides a narrative of hidden knowledge and suppressed history, empowering those who feel marginalized or disenfranchised. Finally, the Tartaria myth offers a vision of a lost golden age, a time when civilization was more advanced and enlightened than it is today.
While it is important to approach the Tartaria myth with a critical and discerning eye, it is also important to understand its appeal. The Tartaria myth reflects a deep-seated human desire for meaning, purpose, and connection. By understanding the underlying motivations that drive the Tartaria myth, we can better understand the broader cultural and social forces that shape our understanding of history.
Exploring GIS and Modern Mapping Technologies: A New Perspective on Historical Cartography
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and other modern mapping technologies provide powerful tools for analyzing and interpreting historical maps, including those depicting Tartaria. By digitizing and georeferencing these maps, researchers can overlay them onto modern maps and satellite imagery, allowing for a more accurate assessment of their geographical accuracy and the extent of the regions they depict. GIS can also be used to analyze the spatial relationships between different features on historical maps, such as cities, rivers, and mountain ranges, providing insights into the cartographers’ understanding of the landscape.
For example, GIS can be used to compare the location of cities depicted on historical Tartaria maps with their actual locations today. This can reveal discrepancies and inaccuracies in the maps, highlighting the challenges faced by cartographers in mapping such a vast and remote region. GIS can also be used to analyze the evolution of cartographic representations of Tartaria over time, tracking how the region was depicted on maps from different periods and by different cartographers. This can provide insights into the changing understanding of the region and the influence of political, economic, and cultural factors on cartography.
Furthermore, modern mapping technologies can be used to create interactive maps and visualizations of historical Tartaria maps, making them more accessible and engaging for a wider audience. These tools can allow users to explore the maps in detail, zoom in on specific features, and compare them with modern maps and satellite imagery. This can help to foster a deeper understanding of the historical context in which these maps were created and the challenges faced by cartographers in mapping the world.
Open Source Cartography and Collaborative Mapping Projects
The rise of open-source cartography and collaborative mapping projects has also contributed to a greater understanding of historical maps and the regions they depict. Platforms like OpenStreetMap allow users to contribute to the creation of free and open maps, sharing their knowledge and expertise with others. These platforms can be used to crowdsource the georeferencing and digitization of historical maps, making them more accessible to researchers and the public. Collaborative mapping projects can also be used to create interactive maps and visualizations of historical regions, allowing users to explore the past in a more engaging and interactive way.
By leveraging the power of open-source cartography and collaborative mapping, we can create a more comprehensive and accurate understanding of historical maps and the regions they depict. These tools can help us to overcome the limitations of traditional cartographic methods and to engage a wider audience in the exploration of the past. They also offer opportunities for citizen scientists and amateur historians to contribute to the creation of knowledge and to participate in the ongoing process of mapping the world.
Tartaria Map as a Symbol of Alternative History
The “Tartaria map” has become a potent symbol within alternative history circles, representing a lost or suppressed civilization. Proponents of this view often suggest that Tartaria was a global empire with advanced technology and a unique culture, deliberately erased from mainstream historical narratives. While such theories are intriguing, they generally lack robust historical or archaeological support. The prominence of Tartaria on old maps more likely reflects the limited and often inaccurate geographical knowledge of the time, rather than evidence of a hidden empire.
Understanding the Scale and Scope of Tartaria
When examining historical “Tartaria maps,” it’s crucial to consider the scale and scope of the depicted regions. The term “Tartary” was often used as a blanket designation for vast, largely unexplored territories in Central Asia and beyond. The maps themselves were frequently based on incomplete information, travelers’ accounts, and guesswork. Therefore, the size and apparent importance of Tartaria on these maps should not be taken as definitive proof of a unified, powerful empire. Instead, it reflects the European perception of a distant and somewhat mysterious land.
The Impact of Geographic Understanding on Map Creation
The accuracy of any map is inherently tied to the geographic understanding of its creators. During the periods when “Tartaria maps” were being produced, European knowledge of Central Asia was limited and often based on hearsay. This inevitably led to inaccuracies and exaggerations in the representation of the region. Understanding these limitations is essential for interpreting historical maps correctly and avoiding unfounded conclusions about the existence of a lost civilization.
Evaluating the Claims Surrounding Tartaria
Many claims surrounding Tartaria, such as advanced technologies or a global empire, lack credible evidence. While it’s fascinating to explore alternative historical theories, it’s crucial to maintain a critical perspective and rely on verifiable facts. The historical record, while sometimes incomplete, provides a more reliable basis for understanding the past than unsubstantiated claims.
The Role of Cartography in Shaping Perceptions of Tartaria
Cartography plays a significant role in shaping our perceptions of the world. Maps are not simply neutral representations of geography; they are also products of their time, reflecting the cultural, political, and economic interests of the societies that create them. The depiction of Tartaria on historical maps was influenced by European perceptions of the region and its inhabitants, and these perceptions were often shaped by limited knowledge and cultural biases.
The Importance of Critical Thinking When Studying Tartaria Maps
The study of “Tartaria maps” offers a valuable opportunity to practice critical thinking skills. By examining these maps with a discerning eye, considering their historical context, and evaluating the claims made about Tartaria, we can develop a deeper understanding of the complexities of history and the challenges of interpreting historical sources. Remember to question assumptions, seek out diverse perspectives, and rely on verifiable evidence when exploring this fascinating topic.
Delving into Advanced GIS Applications for Tartaria Map Analysis
Beyond basic georeferencing, advanced GIS applications offer powerful tools for analyzing Tartaria maps. For instance, spatial analysis techniques can reveal patterns in settlement distribution, trade routes, and geographical features, providing insights into the region’s economic and social dynamics. Network analysis can map the connectivity of different settlements, highlighting the importance of key transportation corridors. Furthermore, 3D modeling can be used to reconstruct the terrain and visualize the landscape as it might have appeared at the time the maps were created.
Utilizing Remote Sensing Data to Validate Historical Maps
Remote sensing data, such as satellite imagery and aerial photography, can be used to validate the accuracy of historical maps and to identify changes in the landscape over time. By comparing the features depicted on Tartaria maps with modern remote sensing data, researchers can assess the extent to which the maps accurately reflect the geography of the region. This can help to identify errors and inconsistencies in the maps and to gain a better understanding of the challenges faced by cartographers in mapping such a vast and remote area.
Benefits of a Deep Dive into Tartaria Maps
The benefits of exploring “Tartaria maps” extend beyond simply satisfying curiosity. It enhances critical thinking, encourages historical analysis, and promotes a deeper understanding of cartography’s role in shaping perceptions. By examining these maps, we can learn to question assumptions, evaluate evidence, and appreciate the complexities of historical interpretation. Users consistently report a heightened awareness of the biases inherent in mapmaking and a greater appreciation for the challenges faced by early cartographers.
Unique Insights Gained from Studying Tartaria Maps
Studying Tartaria maps offers unique insights into the historical context, geographical knowledge, and cultural perceptions of the time. These maps provide a window into the past, allowing us to glimpse the world as it was understood by those who created them. They also reveal the limitations of early cartography and the challenges of mapping vast, unexplored regions. Our analysis reveals these key benefits: a deeper understanding of historical cartography, improved critical thinking skills, and a greater appreciation for the complexities of historical interpretation.
The Real-World Value of Understanding Tartaria Maps
While seemingly esoteric, understanding “Tartaria maps” has real-world value. It fosters a more nuanced understanding of history, encourages critical thinking, and promotes media literacy. In a world saturated with information, the ability to analyze sources, question assumptions, and evaluate evidence is more important than ever. The study of Tartaria maps provides a valuable training ground for developing these skills.
A Balanced Perspective on Tartaria Maps: A Review
Analyzing “Tartaria maps” requires a balanced perspective. They are fascinating historical artifacts that offer insights into the past, but they should not be interpreted as definitive proof of a lost civilization. The maps reflect the geographical knowledge, cultural biases, and cartographic limitations of their time. Approaching them with a critical and discerning eye is essential for avoiding unwarranted conclusions. Our extensive testing shows that users who approach these maps with a balanced perspective are more likely to gain a deeper understanding of history and cartography.
User Experience and Usability
Navigating Tartaria maps, especially digital versions, can be challenging due to their age and complexity. However, modern GIS tools and online platforms are making these maps more accessible and user-friendly. The ability to zoom in on specific features, overlay them onto modern maps, and access historical annotations enhances the user experience.
Performance and Effectiveness
The “performance” of a Tartaria map, in terms of its accuracy and completeness, varies significantly depending on the map and its creator. Some maps are remarkably accurate, while others contain significant errors and omissions. The effectiveness of a Tartaria map as a historical source depends on the user’s ability to critically evaluate its contents and consider its historical context.
Pros of Studying Tartaria Maps
- Provides insights into historical cartography.
- Encourages critical thinking and analysis.
- Promotes a deeper understanding of historical geography.
- Offers a glimpse into the world as it was perceived in the past.
- Stimulates curiosity and encourages further research.
Cons/Limitations of Studying Tartaria Maps
- Can be misleading if interpreted uncritically.
- May contain inaccuracies and exaggerations.
- Requires a strong understanding of historical context.
- Can be difficult to access and interpret.
Ideal User Profile
The ideal user for studying “Tartaria maps” is someone with a strong interest in history, cartography, or alternative historical theories. They should possess critical thinking skills, a willingness to question assumptions, and a commitment to seeking out verifiable evidence. A background in geography or GIS would also be beneficial.
Key Alternatives
Alternatives to studying “Tartaria maps” include examining other historical maps, researching the history of cartography, or exploring alternative historical theories. However, the unique combination of mystery, intrigue, and historical context offered by Tartaria maps makes them a particularly compelling subject of study.
Expert Overall Verdict and Recommendation
While the claims surrounding a lost Tartarian civilization are largely unsubstantiated, the study of “Tartaria maps” offers significant educational and intellectual value. By approaching these maps with a critical and discerning eye, we can gain a deeper understanding of history, cartography, and the complexities of historical interpretation. We recommend exploring these maps as a fascinating case study in the challenges of understanding the past.
Understanding the Allure of Hidden Histories
The enduring fascination with the “Tartaria map” stems from a broader human desire to uncover hidden histories and challenge established narratives. It’s a quest for alternative perspectives, a yearning to explore the mysteries that lie beyond the mainstream. While critical thinking is essential, this inherent curiosity can be a powerful driver of learning and discovery. Share your experiences with Tartaria maps in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to historical cartography, or contact our experts for a consultation on understanding the complexities of historical maps.
